Transmission
COVID-19 is highly transmitted through droplets.
Transmission
Transmission is high when there is contact with symptomatic patients. Asymptomatic transmission and transmission during the terminal stages of incubation period, before patients showing symptoms, have been reported. Thus, in our country contact tracing is done according to WHO recommendation that include people in direct contact with the patient 48 hours before he or she was having any symptoms.
The virus was first thought to be transmitted with contact to animals as most of the patients in local Huhanan market in Wuhan city, Hubei province, China, were seafood and live animals were on market. The disease transmission continued after closure of the market due to human to human transmission. Even though studies are made and information get updated regularly SARS CoV-2 is believed to be transmitted by droplets that are produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes or talks. These droplets because of their size do not stay suspended in the air beyond 2 meter distance.
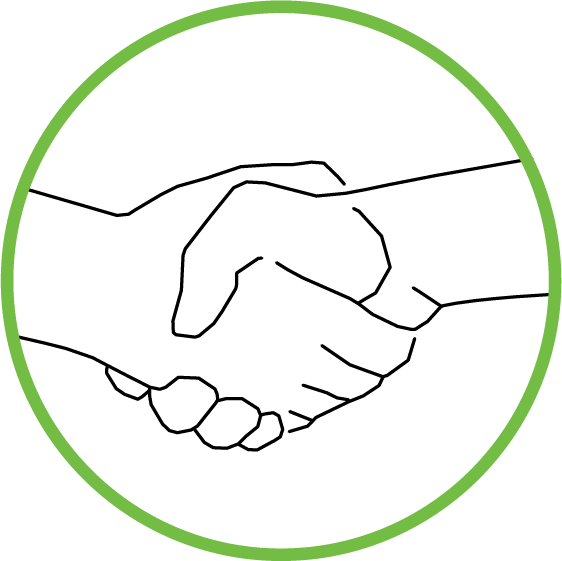

Direct Transmission
Studies have also indicated that the virus can exist on surfaces, that it not only can be transmitted through direct contact with the patients but through contact of contaminated materials in the environment. Hospital related transmission of the virus is still high and WHO warns the virus in these cases can be aerosolized due to invasive procedures done.
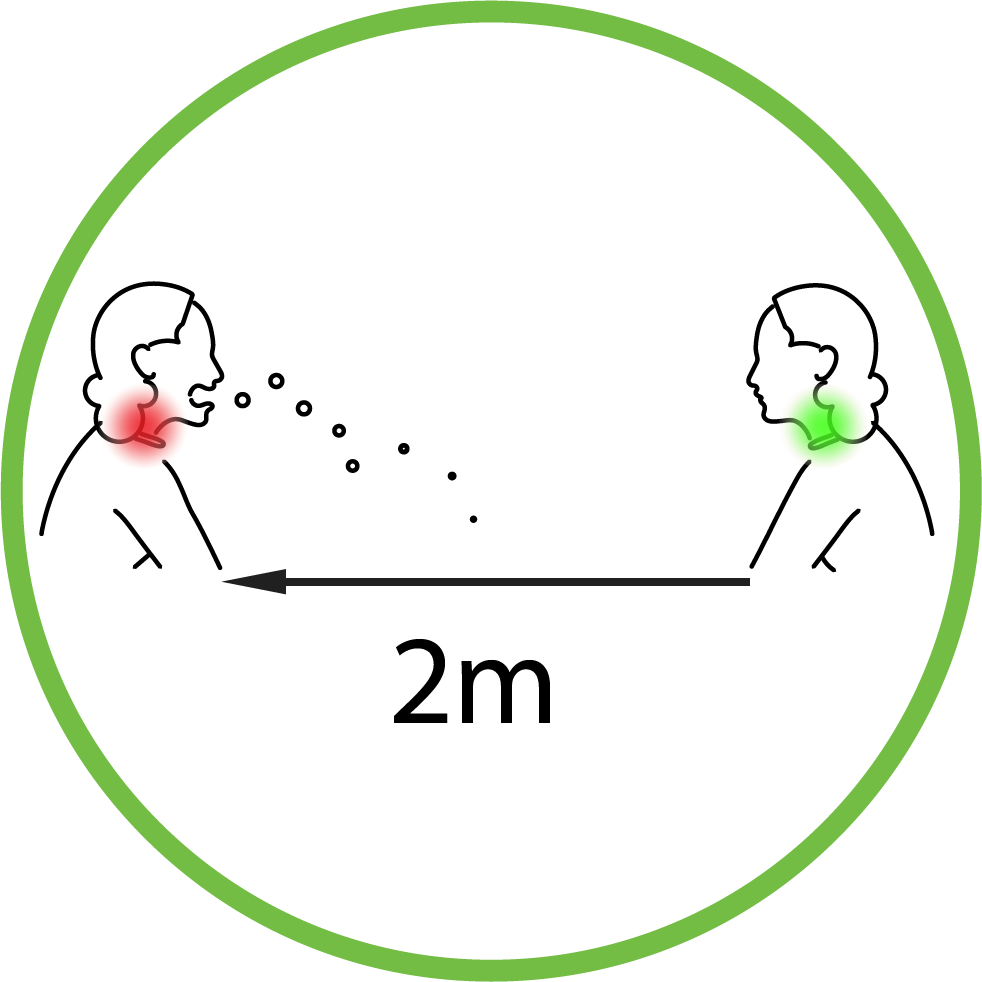
Droplet Transmission
Even though studies are made and information get updated regularly SARS CoV-2 is believed to be transmitted by droplets that are produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes or talks. These droplets because of their size do not stay suspended in the air beyond 2 meter distance.
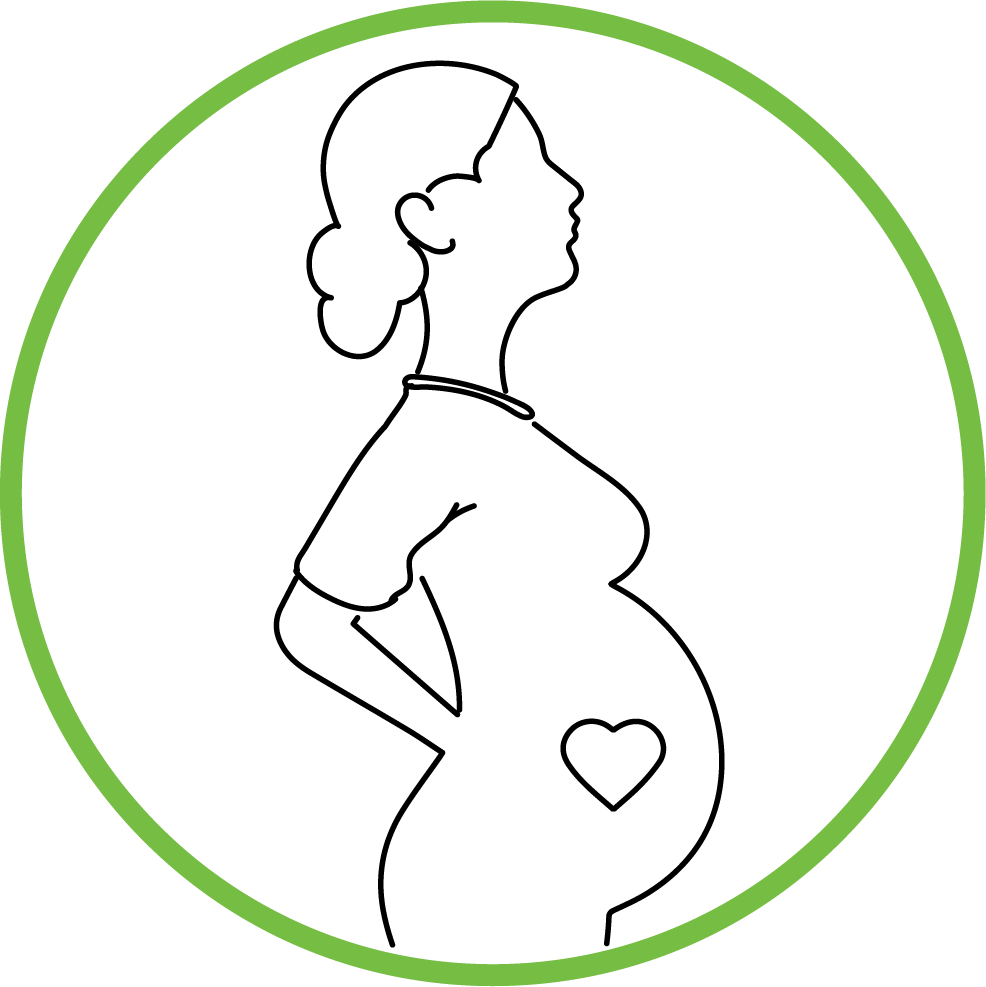
Mother to Child Transmission
Further studies are required to determine vertical transmission and effects of COVID-19 during pregnancy. So far, scientists believe that pregnant women may be more susceptible to COVID-19 since they are vulnerable to respiratory infection. In studies conducted on pregnant woman with COVID -19, no evidence was found on vertical transmission of the virus even though an increased prevalence of preterm deliveries has been noticed.
Other Transmission
The virus has also been isolated from stool, gastrointestinal tract, saliva, urine and secretion from patient’s eyes. Faeco-oral transmission and through direct contact with such body fluids have not been established.
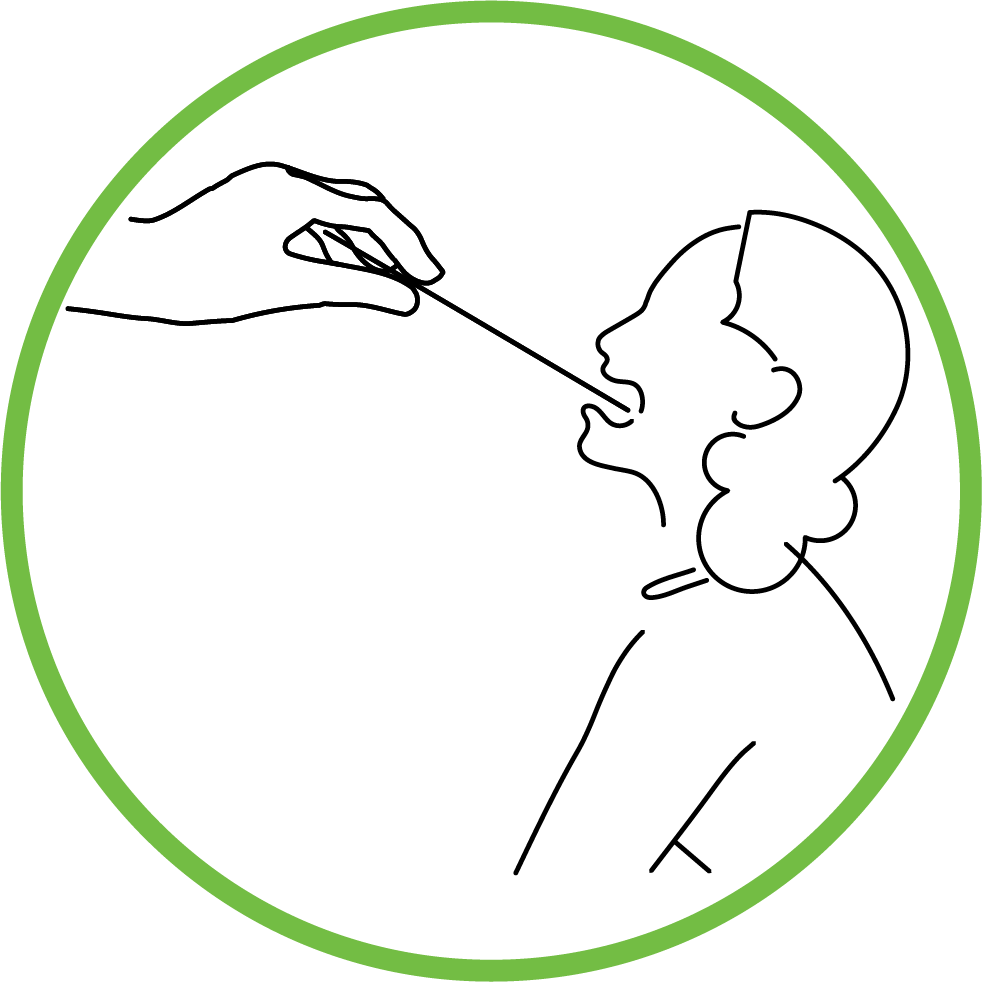
Diagnosis
Early diagnosis, especially in those having acute respiratory distress is essential in management of the disease. The standard non invasive diagnosis of the COVID-19 is through real time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay. Samples are taken from oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airway for conscious patient and from bronchoalveolar lavage for intubated or unconscious patients.
These test can results in false negative based on the sensitivity of the nucleic acid test kit, if there is a fault in collecting samples (source of the sample, method of collection) and if the patients where on an antiviral or hormone therapy.
Other means of diagnosis that are being carried out is combining of imaging features with clinical and laboratory findings.Reports have been made that even asymptomatic patients might have abnormal chest CT findings that can facilitate in early diagnosis of the virus.